Revolutionizing Metal Recycling: Scaling AI-Powered Safety and Purity
- RameshDharmaraj
- 4 days ago
- 3 min read

The metal recycling industry faces a critical challenge: "unwanted items" like lithium-ion batteries and pressurized cylinders can cause catastrophic fires or damage expensive shredders. Manual sorting is often insufficient to catch these hazardous contaminants at scale. By leveraging CircularNet, Google Cloud's AI infrastructure, and Google Maps geospatial intelligence, recyclers can build a robust, predictive system to ensure safety and improve material purity.
1.The Vision Engine: CircularNet & Object Detection
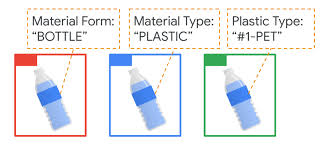
The heart of the system is CircularNet, an open-source machine learning model developed by Google specifically for the circular economy. It is designed to lower the barrier for waste identification and provides high-accuracy detection for materials like metal, paper, and plastic.
Instance Segmentation: CircularNet uses the Mask R-CNN algorithm to precisely outline and classify objects in cluttered waste streams.
Custom Taxonomy: The model can be trained to recognize specific "unwanted items" in metal scrap, such as Lithium-ion Batteries, Gas Cylinders, and Fire Extinguishers.
Predicting Purity: By identifying contaminants like copper in steel piles, the system can predict the quality grade of the final melt, allowing for more accurate pricing and reduced processing errors.
2. Scalable Infrastructure on Google Cloud
To move from a local prototype to an industrial-scale system, the architecture must handle massive data flows and continuous model retraining. Google Cloud provides the necessary MLOps tools to manage this lifecycle.
Component | Role in the Recycling System | Feature Highlight |
Vertex AI Pipelines | Orchestrates the end-to-end workflow from data ingestion to deployment | |
Cloud Storage | Stores raw images from cameras and trained model artifacts | Durable artifact storage |
Pub/Sub & Functions | Triggers retraining when new "unwanted item" images are uploaded to improve detection | Event-driven automation |
Vertex Model Registry | Versions different model iterations to ensure the most accurate safety alerts are live | Model governance |
3. Geospatial Intelligence with Google Maps
Google Maps Platform is not just for navigation; it plays a vital role in predicting where unwanted items might originate and optimizing the logistics of getting scrap to the facility.
Asset & Quality Tracking: Recyclers use the Google Maps API to track incoming scrap shipments. By correlating geographic origin with the detection of contaminants (like batteries), businesses can identify high-risk suppliers or regions.
Route Optimization: The Route Optimization API helps fleet managers plan efficient collection routes, reducing the carbon footprint of scrap transportation.
Predictive Analytics: By mapping historical data of "unwanted items" across locations, the system can predict seasonal trends in hazardous waste disposal, allowing facilities to staff up or adjust safety protocols in advance.
4. Operational Workflow & Real-World Impact
Building this system leads to a "closed-loop" recycling model where purity is high and risk is low. Companies using these technologies have seen up to 90% accuracy in material detection.
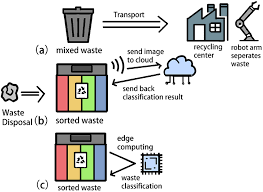
Capture: Cameras mounted above conveyor belts capture high-resolution images in real t ime.
Analyze: Images are sent to a Vertex AI endpoint where a custom-trained CircularNet model scans for hazardous items.
Act: If a battery or cylinder is detected, the system sends instant alerts via WhatsApp or triggers physical removal using air ejection bars.
Optimize: Data on these detections is stored and mapped, helping the business predict future risks and optimize supply chain quality.
Conclusion
The future of metal recycling depends on moving beyond reactive safety measures toward intelligent, data-driven operations. By combining CircularNet’s advanced vision capabilities, Google Cloud’s scalable AI infrastructure, and Google Maps’ geospatial intelligence, recyclers can detect hazardous “unwanted items” before they cause damage, predict material purity with greater accuracy, and continuously optimize their processes.
This integrated, AI-powered approach not only protects people and equipment but also improves operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and increases the overall value of recycled materials. As regulatory pressure and sustainability expectations continue to rise, adopting intelligent recycling systems is no longer optional—it is essential. Organizations that invest today in smart, predictive technologies will be better positioned to build safer facilities, stronger supply chains, and a truly circular economy.
References
CircularNet: Reducing Waste with Machine Learning – Google Research
Vertex AI Documentation – Google Cloud
Google Maps Platform for Logistics & Transportation
Deep Learning-Based Waste Detection in Recycling












Comments